| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 코틀린
- SWIFT
- Nest.js
- Producer
- state
- 반복문
- component
- restful api
- kafka
- node.js
- AWS
- 개발이취미인사람
- Sequelize
- spring boot
- vue
- 상속
- swagger
- props
- Kotlin
- 개발자
- jpa
- file upload
- javascript
- back-end
- react
- 조건문
- It
- front-end
- 개발이 취미인 사람
- java
- Today
- Total
개발이 취미인 사람
[Swagger] Node.js Swagger API 문서화 본문
- 개요
안녕하세요. 이번 시간에는 Node.js API 서버에서 Swagger를 활용한 문서화 작업을 해보는 시간을 가져보도록 하겠습니다.
기본적으로 프론트 앤드와 백앤드 개발자가 작업을 할 때 가장 많이 협업하는 부분은 아무래도 클라이언트와 서버 간에 통신 부분입니다.
예전에는 git이나 구글 doc, wiki 등 텍스트 문자를 통해 API 문서를 정의해 공유했습니다. (보기가 불편하다는 단점이 가장 큰 것 같아요..)
최근에는 Postman을 통해 API를 정의하고 공유하는 방식도 많이 사용합니다. 하지만 우리 API 서버 정보가 Postman 서버에 저장되기 때문에 또 다른 문제가 발생합니다...
이러한 문제를 Swagger를 활용해 자체 API 서버에 연결을 한다면 해결이 가능합니다. 하지만 항상 장점만 있는 건 아니겠죠?
기술은 자신에 상황에 맞게 사용해야 되는 것 같습니다. (이점 꼭 유의하세요!!)
- 선행 학습
기본적으로 Swagger에 대해 모르시는 분들은 아래 링크를 통해 학습하고 오시는 걸 추천드리겠습니다.
[Swagger] Swagger UI를 활용한 내부 API Client 구축
[Swagger] Swagger UI를 활용한 내부 API Client 구축
- 개요 안녕하세요. 이번 글에서는 Swagger UI를 활용한 API 문서화 및 Client 서버 구축에 대해서 알아보겠습니다. 일단 Swagger라는 기술은 API를 설계하고 문서화를 해주는데 도움을 주는 기술입니다.
any-ting.tistory.com
Swagger UI를 활용해서 개별 클라이언트 서버를 구축하는 방식이 아닌 Express 환경에 Swagger를 연결하는 방식으로 진행하겠습니다.
Node Express API 서버를 구축하는 방법을 모르시는 분들은 아래 링크를 통해 학습하고 오시는 걸 추천드리겠습니다.
[Node.js] Express 서버 구축
- 개요 안녕하세요 이번 시간에는 Node.js 웹 애플리케이션 프레임워크인 Express를 활용해서 RESTful API 서버를 구축하는 시간을 가져보도록 해보겠습니다. 기본적으로 Node.js 서버를 PC에 설치를 해야
any-ting.tistory.com
- 설정
Express 서버와 Swagger를 연결하기 위해서는 두 가지 패키지가 필요합니다.
패키지 설치
npm install swagger-jsdoc swagger-ui-express --save-dev
- swagger-jsdoc : jsdoc주석으로 Swagger API 문서를 표현하기 위해 사용
- swagger-ui-express: swagger-ui와 express를 연결하기 위해 사용
Swagger 환경 설정
const swaggerUi = require("swagger-ui-express")
const swaggereJsdoc = require("swagger-jsdoc")
const options = {
swaggerDefinition: {
openapi: "3.0.0",
info: {
version: "1.0.0",
title: "개발이 취미인 남자",
description:
"프로젝트 설명 Node.js Swaager swagger-jsdoc 방식 RestFul API 클라이언트 UI",
},
servers: [
{
url: "http://localhost:3000", // 요청 URL
},
],
},
apis: ["./routers/*.js", "./routers/user/*.js"], //Swagger 파일 연동
}
const specs = swaggereJsdoc(options)
module.exports = { swaggerUi, specs }swagger/swagger.js 파일 생성
환경 설정에서 중요한 부분은 apis 부분입니다.
우리가 실제 Express Router 파일과 Swagger 파일을 연결합니다.
기본 옵션을 다 설정하고 옵션을 index.js에서 연결을 해줍니다.
//express 모듈 불러오기
const express = require("express")
const api = require("./routers")
//express 사용
const app = express()
//Express 4.16.0버전 부터 body-parser의 일부 기능이 익스프레스에 내장 body-parser 연결
app.use(express.json())
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }))
app.use("/api", api)
const { swaggerUi, specs } = require("./swagger/swagger")
app.use("/api-docs", swaggerUi.serve, swaggerUi.setup(specs))
/**
* 파라미터 변수 뜻
* req : request 요청
* res : response 응답
*/
/**
* @path {GET} http://localhost:3000/
* @description 요청 데이터 값이 없고 반환 값이 있는 GET Method
*/
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
//Hello World 데이터 반환
res.send("Hello World")
})
// http listen port 생성 서버 실행
app.listen(3000, () => console.log("개발이 취미인 남자 :)"))app.use("/api-docs", swaggerUi.serve, swaggerUi.setup(specs)) 부분에서 UI와 옵션을 Express Router 환경에 연결합니다.
우리는 /api-docs 경로로 접속하면 아래와 같은 페이지가 보입니다.

위와 같은 화면이 잘 보인다면 기본 설정을 성공했습니다. 그럼 이제 우리는 API 문서화를 진행해보겠습니다.
Routers 설정
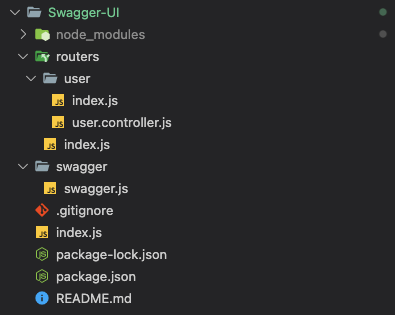
프로젝트 구조는 위와 같습니다.
routers 폴더 아래 user api 정보를 만들어 보겠습니다.
routers 폴더 index.js 파일
const router = require("express").Router()
const user = require("./user")
/**
* @swagger
* tags:
* name: Users
* description: 유저 추가 수정 삭제 조회
*/
router.use("/user", user)
module.exports = router주석 안에 @swagger 태그를 적용하면 해당 주석은 Swagger정보를 작성할 수 있습니다.

Users 태그가 생선 된 걸 알 수 있습니다.
user 폴더 indes.js 파일
const userRouter = require("express").Router()
const userController = require("./user.controller")
/**
* @swagger
* paths:
* /api/user/users:
* get:
* summary: "유저 데이터 전체조회"
* description: "서버에 데이터를 보내지 않고 Get방식으로 요청"
* tags: [Users]
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 전체 유저 정보
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* users:
* type: object
* example:
* [
* { "id": 1, "name": "유저1" },
* { "id": 2, "name": "유저2" },
* { "id": 3, "name": "유저3" },
* ]
*/
userRouter.get("/users", userController.getUsers)
/**
* @swagger
* /api/user/user?user_id={user_id}:
* get:
* summary: "특정 유저조회 Query 방식"
* description: "요청 경로에 값을 담아 서버에 보낸다."
* tags: [Users]
* parameters:
* - in: query
* name: user_id
* required: true
* description: 유저 아이디
* schema:
* type: string
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다. (유저 조회)
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* users:
* type: object
* example: [{ "id": 1, "name": "유저1" }]
*/
userRouter.get("/user", userController.findOneUser1)
/**
* @swagger
* /api/user/{user_id}:
* get:
* summary: "특정 유저조회 Path 방식"
* description: "요청 경로에 값을 담아 서버에 보낸다."
* tags: [Users]
* parameters:
* - in: path
* name: user_id
* required: true
* description: 유저 아이디
* schema:
* type: string
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다. (유저 조회)
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* users:
* type: object
* example: [{ "id": 1, "name": "유저1" }]
*/
userRouter.get("/:user_id", userController.findOneUser2)
/**
* @swagger
*
* /api/user/add:
* post:
* summary: "유저 등록"
* description: "POST 방식으로 유저를 등록한다."
* tags: [Users]
* requestBody:
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다. (유저 등록)
* required: true
* content:
* application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* id:
* type: integer
* description: "유저 고유아이디"
* name:
* type: string
* description: "유저 이름"
*/
userRouter.post("/add", userController.createUser)
/**
* @swagger
* /api/user/update:
* put:
* summary: "유저 수정"
* description: "PUT 방식을 통해 유저 수정(전체 데이터를 수정할 때 사용함)"
* tags: [Users]
* requestBody:
* description: 유저 수정
* required: true
* content:
* application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* id:
* type: int
* description: "유저 고유아이디"
* name:
* type: string
* description: "유저 이름"
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다.(유저 수정)
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* data:
* type: string
* example:
* [
* { "id": 1, "name": "유저1" },
* { "id": 2, "name": "유저2" },
* { "id": 3, "name": "유저3" },
* ]
*/
userRouter.put("/update", userController.setUsers)
/**
* @swagger
* /api/user/update/{user_id}:
* patch:
* summary: "유저 수정"
* description: "Patch 방식을 통해 특정 유저 수정(단일 데이터를 수정할 때 사용함)"
* tags: [Users]
* parameters:
* - in: path
* name: user_id
* required: true
* description: 유저 아이디
* schema:
* type: string
* requestBody:
* description: 유저 수정
* required: true
* content:
* application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* name:
* type: string
* description: "유저 이름"
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다. (유저 수정)
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* data:
* type: string
* example:
* [
* { "id": 1, "name": "유저1" },
* { "id": 2, "name": "유저2" },
* { "id": 3, "name": "유저3" },
* ]
*/
userRouter.patch("/update/:user_id", userController.setUser)
/**
* @swagger
* /api/user/delete:
* delete:
* summary: "특정 유저 삭제"
* description: "요청 경로에 값을 담아 서버에 보낸다."
* tags: [Users]
* parameters:
* - in: query
* name: user_id
* required: true
* description: 유저 아이디
* schema:
* type: string
* responses:
* "200":
* description: 사용자가 서버로 전달하는 값에 따라 결과 값은 다릅니다. (유저 삭제)
* content:
* application/json:
* schema:
* type: object
* properties:
* ok:
* type: boolean
* users:
* type: object
* example:
* [
* { "id": 1, "name": "유저1" },
* { "id": 2, "name": "유저2" },
* { "id": 3, "name": "유저3" },
* ]
*/
userRouter.delete("/delete", userController.delUser)
module.exports = userRouter실제 router를 연결하는 부분에 Swagger 문서를 작성하기만 하면 문화는 완료됩니다.

제대로 설정했다면 위와 같이 Swagger API 만들 수 있습니다.
여러분도 직접 작성해 구축해보는 걸 추천드리겠습니다.
이번 시간에는 Express API 서버에서 Swagger를 연결하는 시간을 가져봈습니다. 감사합니다 :)
- GitHub
swagger-jsdoc 브런치를 확인해주세요 :)
https://github.com/Ryan-Sin/Swagger-UI/tree/swagger-jsdoc
GitHub - Ryan-Sin/Swagger-UI
Contribute to Ryan-Sin/Swagger-UI development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'백앤드(Back-End) > Swagger' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Swagger] Swagger Yaml 파일 RESTFul API 클라이언트 구축 (0) | 2021.01.28 |
|---|---|
| [Swagger] Swagger Yaml 기본 파일 작성 (0) | 2021.01.12 |
| [Swagger] Swagger UI를 활용한 내부 API Client 구축 (0) | 2021.01.11 |




